Last Updated on December 2, 2022 by Mansoor Abbasi
The electrical consumer units are the main controllers and distributors of energy supply in your property, a house, a building, or a factory. The consumer unit is present near where the electrical wire enters from the mains in most properties. It is an essential component of the electric supply in your home, and you should understand it thoroughly to prevent an accident or electrical hazard. In this article, you’ll completely understand the consumers unit.
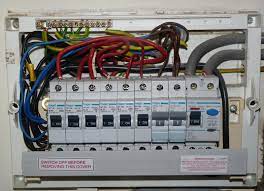
Consumers Unit
First, we need to answer the question “What is a consumer unit?” Consumer units supply electricity to all the circuits in your home. Therefore, it is composed of several different components, all of which are responsible for their part of the system. Familiarizing yourself with these components is essential to understanding how your consumer unit functions and how it may encounter problems in the future.
All of the circuits in your home are powered by the consumer unit, which comprises numerous components, each of which has a specific duty. It’s essential to become familiar with these components to comprehend how your consumer unit functions and any potential issues it might experience.

How the consumer unit works?
There are several types of components in the consumer unit of a home, including the main switch, residual current devices (RCDs), and circuit breakers. Keeping track of your consumer unit’s location should always be done in an emergency. Likewise, it would help if you always turned the facility on or off in an emergency.
What are the types of electrical consumer units?
Consumer units for electrical power perform the same functions, but they differ in size and capacity. The most common types are:
- Consumer Unit with Dual RCDs: This unit is very cost-effective. A pair of RCDs and several MCBs is included. Together, they create ten to fifteen ways to connect.
- Consumer Units Split Load: These units usually contain the main switch and an RCD, with the MCBs placed on the RCD side and the RCBOs on the primary switch side.
- High Integrity Consumer Units: These units are of the most straightforward design, making them easier to install. The circuits are separated effectively, therefore providing good protection.
- RCD Consumer Unit: These consumer units are smaller and have a smaller capacity. They are perfect for your garage, outside storage shed, or garden shade if you want separate consumer units. As the main building is not as large, you do not need a larger consumer unit. The smaller units will do the job just fine. Most of these are two-way or five-way units.
- Populated Consumer Unit: Populated units include all the devices, including the main switch, dual RCDs, and MCBs. No additional parts are required during installation, saving time and money. Typically, populating units cost between £30 and £230.
- Garage Consumer Units: Garage consumer units are much smaller and are typically used for exterior buildings such as garages, sheds, and extensions that require a separate fuse box.
What to consider when choosing a consumer unit?
Read more:An Ultimate Guide About Different Types Of Transformer With Proper Description
A consumer unit is selected based on the following parameters:
1. Protection level
The unit must be protected against dust infiltration. This protection level will prolong the equipment’s lifespan and ensure its safety. A fuse box with an IP40 rating will do the trick.
2. Composition
The halogen-free status of your consumer unit is significant. To prevent toxic gases from spreading during a fire, the structure should be designed to prevent the spread of flames. Metal types can also be chosen if you wish. However, they are more expensive. You can use halogen-free plastic consumer units instead. The cover and body of the unit should also be tested for the fire resistance temperature.
3. Installation and location
In order to choose between flush and surface mounting, you must first decide what kind of unit you require. An elegant flush mount will appeal to your eye first. The installation will be easier with the surface-mounted model if flush mounting is impossible. Your distribution unit’s model can be determined by the location where it will be installed.
4. A DIN-rail unit
If a din rail is placed inside a consumer unit, you should be cautious. Some manufacturers only provide the enclosure.
5. The door
There are two types of enclosure doors, opaque and transparent. A transparent door permits the elements inside to be seen from the outside but not from the inside. Such doors are more secure than opaque doors as well. The transparent doors allow you to see any issues that might occur inside the box. Depending on the room’s requirements, a decorative model might also be optimal. (For example, you can choose a model that suits the ambiance of the art gallery.)
6. Entryways for cables
To maximize your chances of success during installation, you should examine the cable entry points and holes.
7. Sizes
Consider what elements you will use in the electrical consumer unit, as well as the size of the unit according to your space. It’s common to hear terms such as 12 and 24 modules when selecting a consumer unit.
As a reminder, the module concept refers to the width of a miniature circuit breaker. It is possible to install 12 pieces of 1-pole MCBs side by side to MCB. Depending on the number of elements in your installation, you should determine your box dimensions. We recommend that you leave some moduli spaces if the building needs to be expanded in the future and if the fuses emit heat. In this way, extra space will be available if any future additions are needed.
Is plastic a viable option for consumers?
Additionally, a new consumer unit is made out of plastic on the market at comparable prices to new vinyl. As long as they meet current regulations, any old plastic consumer device can still be purchased, and only the casing needs to be replaced.
Cost of Consumer Unit Maintenance
A common problem for homeowners is the discovery of faults in their electrical supply that can easily result in a deadly fire if ignored. To ensure your consumer units are not defective, it’s a good idea to perform a periodic test every five or ten years. The average price for an electrical maintenance check is between £100 and £300. PAT testing, which typically costs between £1 and £2 per item, is a popular maintenance check that includes checks on all electrical appliances.